|
Calibration of the disc diffusion test and determination of
optimal disc content for routine antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
From the
SRA experience it was clear that interpretive zone diameter
breakpoints could be determined corresponding to MIC limits set
by reference authorities for individual bacterial species using
SRA, single strain regression analysis. This means, in fact, that
the disc diffusion test CAN BE CALIBRATED, not only for drug-bug
combinations but also for individual laboratories. Calibration procedures
have been routine tasks in clinical chemistry laboratories for decades.
Examples of calibration procedures using SRA will be given.
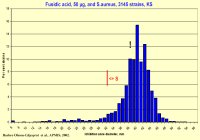
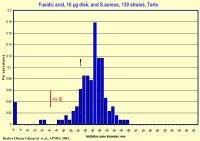
When a clinical microbiology laboratory in Tartu, Estonia, wanted
to set up
fusidic acid disc diffusion tests for isolated Staphylococcus
aureus strains, they used the NCCLS standard which lacked zone breakpoints
for this antibiotic. On the other hand, SRGA issued both MIC limits
and zone interpretive breakpoints, the latter though for a disc
content of 50 µg. In Tartu they wanted to use a lower disc
concent, 10 µg. The solution was to calculate the new zone
breakpoints using SRA.
Another example provided zone breakpoints for some anaerobic species
and
trovafloxacin susceptibility. Although this fluoroquinolone
is not available on the market, the procedure can be applied to
other new antimicrobials at some stage in the clinical testing.
There are often arguments regarding disc contents for routine clinical
laboratory disc testing. The power of SRA calculations can actually
provide a new definition of the optimal disc content for diffusion
tests:
"The lowest disc content of an antibiotic which will
distinguish resistant strains of any bacterial species from strains
of the intermediate or susceptible category."
This is possible to determine using SRA as was shown for
fusidic acid and S.aureus , for
trovafloxacin and aerobic pathogens , and for
trovafloxacin and anaerobes.
Calibration was a valuable feature of SRA, the equation obtained
from original formulae describing the disc diffusion test. A further
extension of the SRA equation leads to the so called M-test, where
you can determine the MIC value of an isolate using several disc
contents,
(see next page).
NEXT 
|